Exploring the Versatility and Applications of Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam: An Innovative Material for Modern Industry
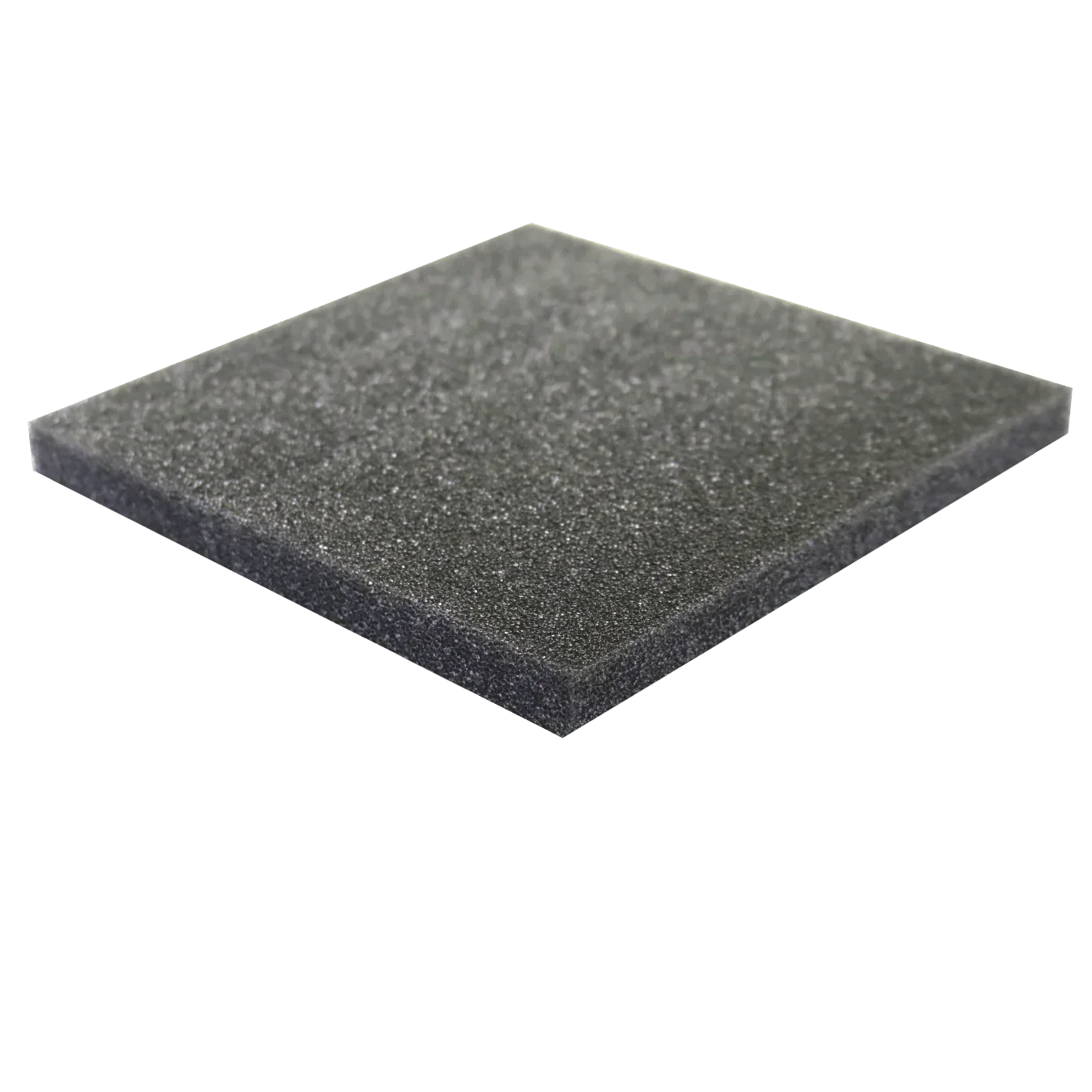
XLPE, or chemically crosslinked Polyethylene foam, is a high-quality material known for its finely closed-cell structure and smooth surfaces on both sides. Cross-linked polyethylene foam has several unique properties that suit various applications. It's a lightweight, flexible, and soft material yet boasts intense, challenging, and resilient physical properties.
The foam retains its shape and thickness over time, even under constant pressure or exposure to harsh environmental conditions. This stability makes it an ideal material for uses that require consistent performance and durability.
XLPE generally provides superior thermal stability and insulation capabilities and is resistant to moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. It also maintains improved dimensional consistency and tranquility, making it ideal for various fabrication methods and user conditions.
This material is effortless to shape, making it perfect for fabrication and thermoforming tasks; in industries such as construction and building, XLPE foams excel due to their low moisture permeability, high buoyancy, and excellent thermal insulation abilities - all critical attributes for managing sound, vibrations, and temperature.
Typically, when contrasted with non-crosslinked polyethylene foam, it provides enhanced thermal stability and insulation properties.
Additionally, it offers better dimensional uniformity and stability across various manufacturing techniques and conditions encountered by the end user.
XLPE Foam represents an unmatched blend of exceptional resilience and unlimited aesthetic appeal. XLPE is a remarkably robust and stiff material, ensuring the safety of goods without causing any damage to painted surfaces.
Practical Applications and Uses of Advanced Technology:
Cross-linked Polyethylene Foam (XLPE) is a versatile material with numerous applications across various industries.
Its versatility allows it to be used across numerous applications, but it shines particularly in influencer kits and various marketing materials. In these contexts, the assurance of safe delivery, the excitement of unboxing, and the display’s visual appeal are all important, and XLPE handles them well.
Here are a few examples:
1. Automotive Industry: XLPE is used for insulation, padding, and sealing in various parts of vehicles. It's used in areas like door panels, headliners, and seating to provide comfort, reduce noise, and offer insulation.
2. Packaging: XLPE foam is an excellent packaging material due to its superior cushioning properties. It protects sensitive equipment during shipping, including electronics, medical devices, and other fragile items.
3. Sports Equipment: Owing to its impact absorption and lightweight characteristics, XLPE is used to manufacture protective gear, such as helmet liners, body armor, and padding in sports equipment.
4. Construction and Building: XLPE foam is used as an insulating material for its thermal and acoustic insulation properties. It's also used underlay for flooring and as a protective barrier on roofs and walls.
5. Electronics: The foam's excellent insulating properties make it ideal for use in electronics, as it can protect delicate components from heat, electricity, and shock damage.
6. Medical: XLPE foam is used in medical devices and equipment for its cushioning and insulating properties. It's used in orthopedic braces, prosthetic liners, and hospital bed padding applications.
7. Marine and Aerospace: Its resistance to water, corrosion, and excellent buoyancy characteristics make XLPE valuable foam in marine applications. In the aerospace industry, it's used for its lightweight, durable, and insulating properties.
8. HVAC systems: Because of its excellent thermal insulation properties, XLPE is used in HVAC systems to insulate ducts and pipes.
9. Case Insert: Foam case inserts are precision-cut pieces of foam designed to fit inside a protective case, with cutouts to hold specific items. They are often used to secure, protect, and organize delicate or expensive equipment, such as cameras, musical instruments, medical devices, electronics, and firearms.
10. Decorative packaging: Cross-linked polyethylene foam (XLPE) is uniquely positioned due to its attractive features like Jewelry and gift boxes.
An Insight into Advanced Foam Cutting Capabilities
TCH offers a variety of cutting methods for cross-linked polyethylene foam. Some of these cutting methods include:
This method is the simplest and quickest for projects with lower volumes and larger-sized products. A hydraulic flatbed press is typically essentially employed for more complex and thicker materials.
The process is versatile, converting both sheet and roll-form materials. It's among the best die-cutting machines for creating die cuts on laminates and sheets.
Flatbed die cutting is used in various industries such as packaging, printing, and manufacturing to cut, crease, emboss, waste strip, and blank separately in a single pass. It's often used for larger orders that require precision and uniformity, especially in the paper, leather, rubber, plastic, and cardboard industries.
Here's how it works:
1.A flatbed die cutter is essentially a large press, so the die (a custom-shaped blade) is mounted onto a flat surface.
2. The material to be cut is placed on a flat surface. This material is often fed from a roll or sheet into the press.
3. The press then applies pressure, pushing the material into the die. This cuts the material into the shape of the die.
4. After the cutting process, the cut material (now called the "blank") is often transported to another area of the machine for further processing, such as folding or gluing.
Flatbed die-cutting machines vary widely in size and complexity, depending on the job's requirements. The dies used in these machines are usually made from steel rule dies, custom designed and manufactured to match the product's exact specifications.
Note that there are other types of die cutting, such as rotary die cutting, which may be a better fit for specific applications. The choice between flatbed and rotary die cutting often depends on factors like the material being used, the complexity of the cut, the required precision, and the production speed.
Waterjet cutting:
Waterjet cutting is used to cut materials using a high-pressure jet or a mixture of water and an abrasive substance. The process allows for precise cutting of various materials, including metal, glass, stone, and plastics.
In pure waterjet cutting, only water is used to perform the cutting, and this method is typically used for softer materials like rubber or foam.
On the other hand, abrasive waterjet cutting involves adding fine particles of hard, abrasive materials (like garnet or diamond) to the water stream to aid in the cutting process. This method uses more complex materials such as metal, glass, or ceramics.
One of the critical advantages of waterjet cutting is that it doesn't generate heat, meaning it won't alter or damage the areas around the cut. This makes it ideal for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures. It also allows for high precision and the ability to cut complex shapes.
Other benefits include its versatility in cutting a wide range of materials, the ability to cut very thick materials, and the minimal need for finishing after the cut, as it leaves a clean edge. It's widely used in manufacturing, engineering, and design.
You may also like: